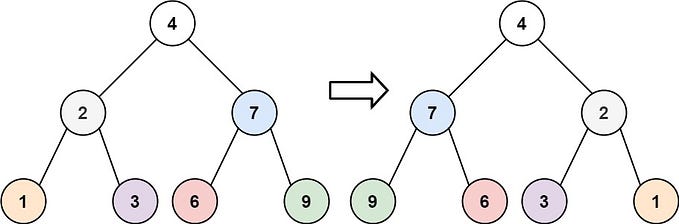
Binary Tree
Binary tree is a tree data-structure, it’s made of nodes where each node has 2 child, left child and right child (or left reference and right reference ).
Thus, binary tree has following parts.
- Root node.
- left child or left reference.
- right child or right reference.

Terminology
- Node: It contains the data also called leaf.
- Root: A tree’s topmost node.
- Parent: Each node (apart from the root) in a tree is parent if it contain max two or minimum one child node.
- Child: If a node has a parent node than is a child node.
- Leaf Node: nodes have no child node or last/end nodes of tree.
- Internal Node: As the name suggests, these are inner nodes with at least one child.
- Depth of a Tree: The number of edges from the tree’s node to the root is.
- Height of a Tree: It is the number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf. The tree height is also considered the root height.
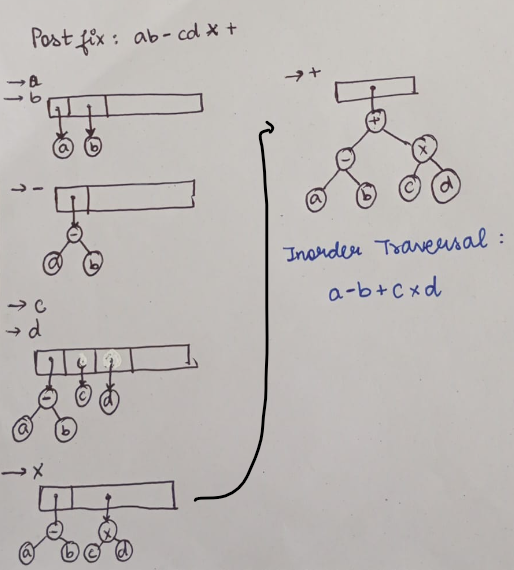
Tree Traversal
A traversal is a process that visits all the nodes in the tree. Since a tree is a nonlinear data structure, there is no unique traversal. We will consider several traversal algorithms with we group in the following two kinds
- depth-first traversal
- breadth-first traversal
There are three different types of depth-first traversals, :
- PreOrder traversal — visit the parent first and then left and right children;
- InOrder traversal — visit the left child, then the parent and the right child;
- PostOrder traversal — visit left child, then the right child and then the parent;
There is only one kind of breadth-first traversal — the level order traversal. This traversal visits nodes by levels from top to bottom and from left to right.
Type of Binary Tree
- Full Binary Tree
- Complete Binary Tree
- Perfect Binary Tree
- Balanced Binary Tree
- Degenerate Binary Tree